Many people underestimate the spring sun because spring is often seen as a transitional period from winter to summer. The sun may be shining, but the temperatures are still pleasantly cool and many people don't think about UV radiation. Even on cloudy days, up to 80 percent of UV rays penetrate through the clouds. It is therefore a common misconception that you don't need sun protection on such days.
Even when the wind is cool or temperatures are low, UV radiation can still be intense and damage the skin. It is therefore important to be aware that the spring sun is no less dangerous than the summer sun. Responsible exposure to the sun doesn't just start in midsummer, but as early as spring. If you protect your skin early, you can reduce long-term skin damage, premature skin ageing and the risk of skin cancer.
The risks and consequences of intense spring sunshine
UV radiation can be very harmful to our skin. There are two main types of UV rays: UV-A and UV-B. UV-A rays penetrate deep into the skin and can accelerate skin ageing. They are strong all year round, even in spring. UV-B rays, on the other hand, are responsible for sunburn and can damage the upper layers of the skin. Both types of rays can increase the risk of skin cancer.
In spring, UV radiation is often just as intense as in summer, even if it is not as hot. It is therefore important to be aware that sunbathing in spring is not without risk.
Short-term consequences of UV radiation
These often occur quickly and can be very unpleasant:
- Sunburn: One of the most common forms of short-term damage is sunburn. The skin becomes red, hot and painful. In severe cases, blisters can form. Sunburn can occur after just a few hours of unprotected sun exposure and can lead to significant discomfort.
- Skin irritation: Even without visible sunburn, the skin can be irritated by UV radiation. This can manifest itself in the form of itching, dryness and a feeling of tightness.
- Sun allergy: Some people develop an allergy to the sun, which manifests itself as itchy redness, blisters or wheals. This can occur particularly in spring, when the skin is more sensitive after the winter.
- Eye damage: UV radiation can also damage the eyes, especially the cornea and conjunctiva. Acute consequences can be conjunctivitis or snow blindness, a type of painful sunburn of the eyes.
Long-term consequences of UV radiation
The long-term effects of UV radiation are often more serious and can cause long-term health problems:
- Skin ageing: In the long term, UV radiation accelerates skin ageing. The skin loses elasticity, becomes thinner and wrinkles and age spots appear early. This process is also known as "photoaging".
- Skin cancer: One of the most serious long-term damages caused by UV radiation is the increased risk of skin cancer.
- Actinic keratoses: These precursors of skin cancer manifest themselves as rough, scaly patches on the skin caused by years of exposure to the sun. If left untreated, they can develop into skin cancer.
- Eye problems: Long-term exposure to UV radiation can also seriously damage the eyes and lead to diseases - such as cataracts - which can significantly impair vision.
Protective measures against the intense spring sun
To protect yourself from the harmful effects of the spring sun, there are various measures that can be easily integrated into everyday life:
- Use sunscreen: Always apply a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) before going outside. An SPF of at least 30 is recommended to ward off both UV-A and UV-B rays. Don't forget to apply a generous amount of sunscreen to all uncovered areas of skin, such as your face, ears, neck and hands. Reapply after swimming or sweating.
- Seek shade: Try to avoid direct sunlight, especially during midday when UV rays are strongest (between 10am and 4pm). If you are outdoors, stay in the shade, under a tree, a parasol or a canopy.
- Wearing sunglasses: Quality sunglasses with UV protection are also important to protect your eyes from harmful radiation.
- Wear protective clothing: Wear clothing that covers your skin, such as long-sleeved shirts, long pants and wide-brimmed hats.
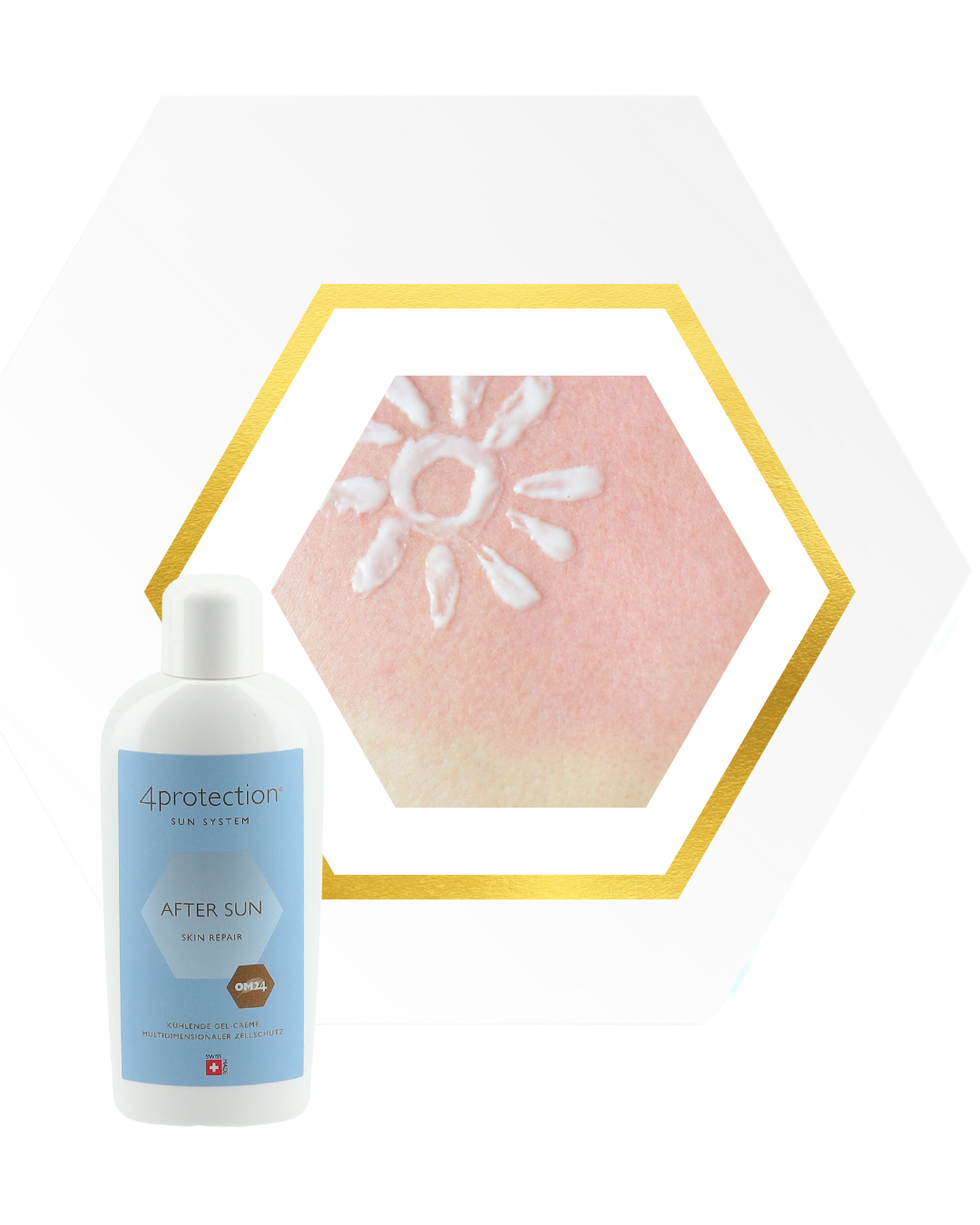
- Use aftersun: After a day in the sun, it is important to soothe and regenerate the skin. Aftersun lotions provide intensive moisture, which helps to restore suppleness to skin that has been dried out by the sun. Apply to cleansed skin after showering and massage in gently. This promotes the regeneration of skin cells and soothes redness and irritation.
Different skin types react differently to the sun, so it is important to adapt your sun protection accordingly:
- Fair skin: People with fair skin have less melanin and are more susceptible to sun-related skin damage. They should always use a high SPF (30 or higher) and take extra care when outdoors. Light-colored clothing and hats are particularly important here.
- Dark skin: Even if darker skin types have more melanin and are less likely to get sunburned, they still need sun protection. UV radiation can also cause damage and skin cancer in darker skin. An SPF of at least 15 is recommended and protective clothing is also important.
- Children: Children have more sensitive skin, which is particularly susceptible to UV damage. Use special sunscreens for children that are suitable for their sensitive skin and make sure they reapply regularly. Protective clothing and hats are particularly important for children.
- Older people: With increasing age, the skin becomes thinner and more sensitive to UV rays. Older people should therefore use a high SPF and wear protective clothing. Regular skin examinations are also important to detect early signs of skin damage or skin cancer.
By following these protective measures and paying attention to the specific needs of your skin type, you can minimize the damaging effects of the intense spring sun and keep your skin healthy.
OM24®: Support in the fight against UV damage
OM24® is a natural complex of substances from the Camellia Sinensis tea plant, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This can help to protect the skin and body from harmful environmental influences, regenerate the cells and counteract premature cell ageing.
Through regular and targeted care with OM24®, you can help your skin to counteract sun damage - such as "photoaging" - and improve the appearance of premature wrinkles and pigmentation spots.

See the impressive difference here: thanks to the daily use of OM24®-sun cream, the pigment spots have been significantly reduced.
With OM24® you can effectively protect yourself from the harmful effects of the spring sun and give your skin the care it deserves.
Conclusion
The spring sun is often underestimated, although its UV radiation can be just as strong as in summer. Short-term consequences such as skin irritation occur quickly, while long-term damage such as premature skin ageing and skin cancer only become apparent years later. Protective measures such as sunscreen, protective clothing and breaks in the shade are essential and should be adapted to the skin types. OM24® can also help to protect and regenerate the skin.
Enjoy your first sunbath of the year, but do it wisely and with the right protection to keep your skin healthy.